WORKSHOP PAPER
Quantum Efficiency and Optical Cross-talk of Pixels with Backside Scattering Technique for Near-Infrared Imaging
Abstract
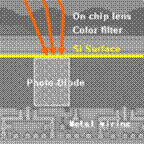
We present performance of image sensor pixel with the structure of surface-limited local trench array to achieve backside scattering technique (BST), to enhance quantum efficiency of CMOS image sensor, especially at near-infrared wavelength. The pixel with BST structure of selection is demonstrated to exhibit significant improvement of quantum efficiency at 940nm, 1.5 times higher than that of pixel without BST, with acceptable inter-pixel cross-talk.Keywords
Quantum Efficiency, Optical Cross-talk, Backside Scattering Technique,References
1) J. Park et al., "Pixel Technology for Improving IR Quantum Efficiency of Backside-illuminated CMOS Image Sensor", Proc. International Image Sensor Workshop, 2019. https://doi.org/10.60928/8g5j-6qbt
2) J.K. Lee et al., "A 2.1 e- Temporal Noise and -105 dB Parasitic Light Sensitivity Backside-Illuminated 2.3 μm Pixel Voltage-Domain Global Shutter CMOS Image Sensor Using High-Capacity DRAM Capacitor Technology", 2020 ISSCC Dig. Tech. Pap. I., 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/isscc19947.2020.9063092
3) J.C. Ahn et al., "A 1/4-inch 8Mpixel CMOS Image Sensor with 3D Backside-Illuminated 1.12 μm Pixel with Front-Side Deep-Trench Isolation and Vertical Transfer Gate", 2014 ISSCC Dig. Tech. Pap., 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/isscc.2014.6757365
4) X. Xie et al., "Regularized Slanted-Edge Method for Measuring the Modulation Transfer Function of Imaging Systems", Appl. Optics, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.57.006552
5) R. Fontaine et al., "A Survey of Enabling Technologies in Successful Consumer Digital Imaging Products", Proc. International Image Sensor Workshop, 2017